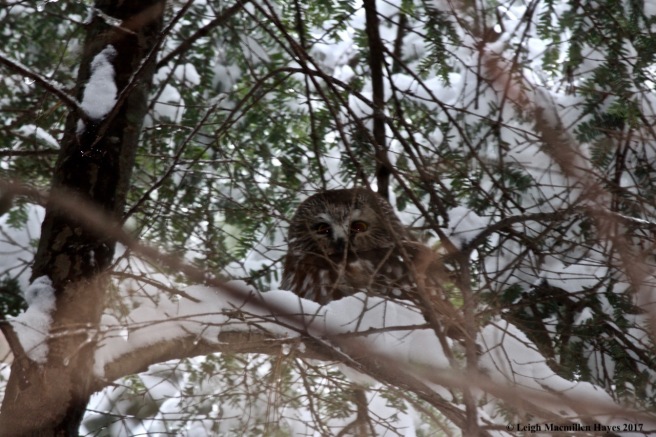
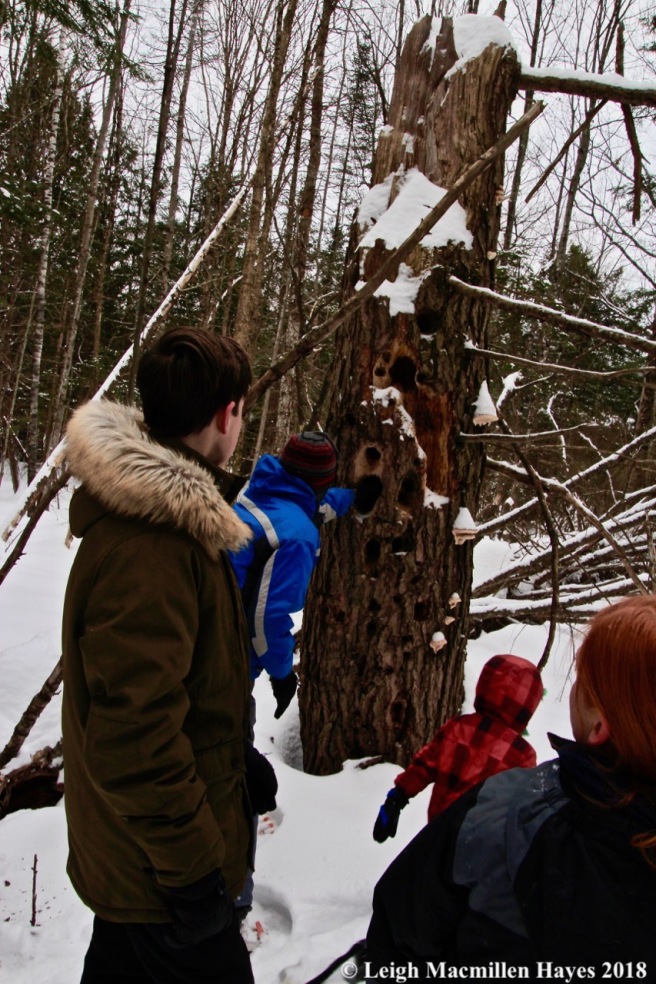
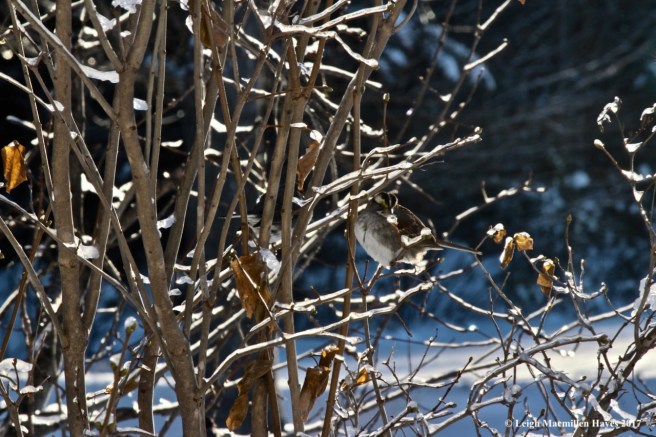
According to a Cherokee legend, one cold season an injured sparrow knew he could not fly south with his family, so he bid them farewell and went in search of a place to survive.
Sparrow asked Oak to shelter him among its leaves so he might heal and greet his family upon their return in the spring.
But being a crusty old tree, Oak didn’t wish to have a winter house guest and so he turned Sparrow away.
Downtrodden, Sparrow approached Maple. Sweet as she might be, Maple also turned Sparrow away.
And so it went. Sparrow was turned down by each tree he visited, until there was only Pine left to ask for help.
Pine listened to Sparrow’s pleas and his heart heard Sparrow’s plight. And though Pine knew his leaves were tiny and more like needles, and his branches not as many as the others, he welcomed Sparrow to join him for the cold season.
As hoped, Sparrow healed and greeted his family the following spring.
Creator heard and saw all that had happened and called a great council of the Trees. In his address, he rebuked them for they’d been given so much and would not share the least of what they had with Sparrow in his time of need. Therefore, from that day forward, when cold came upon the land, their leaves would wither, die and blow away.
Creator then spoke to Pine, praising him for being the least among the trees, and yet giving so much. And so, Pine was honored to remain forever green.
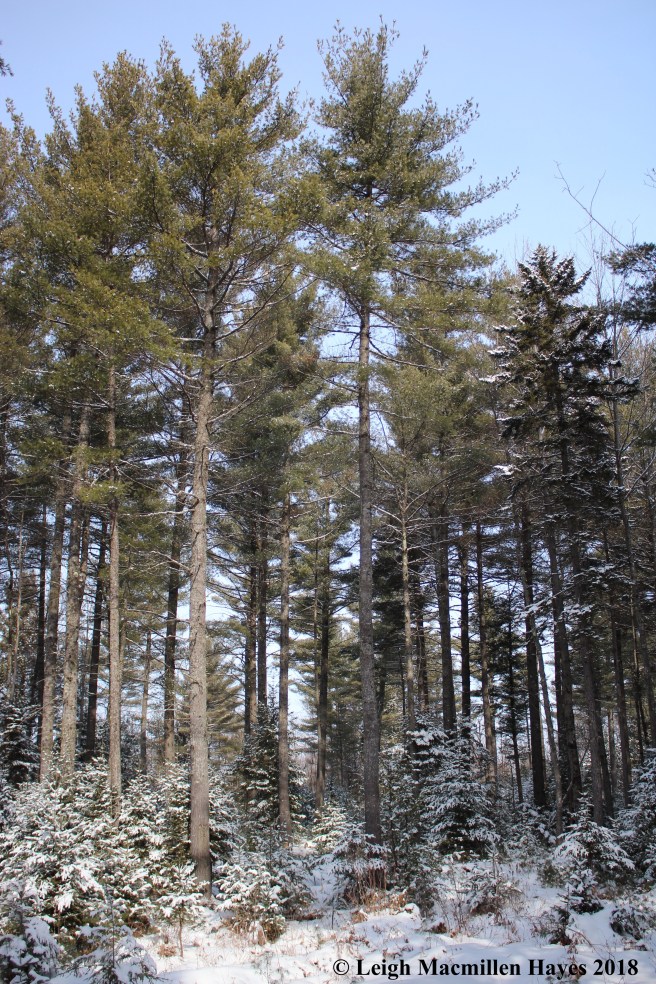

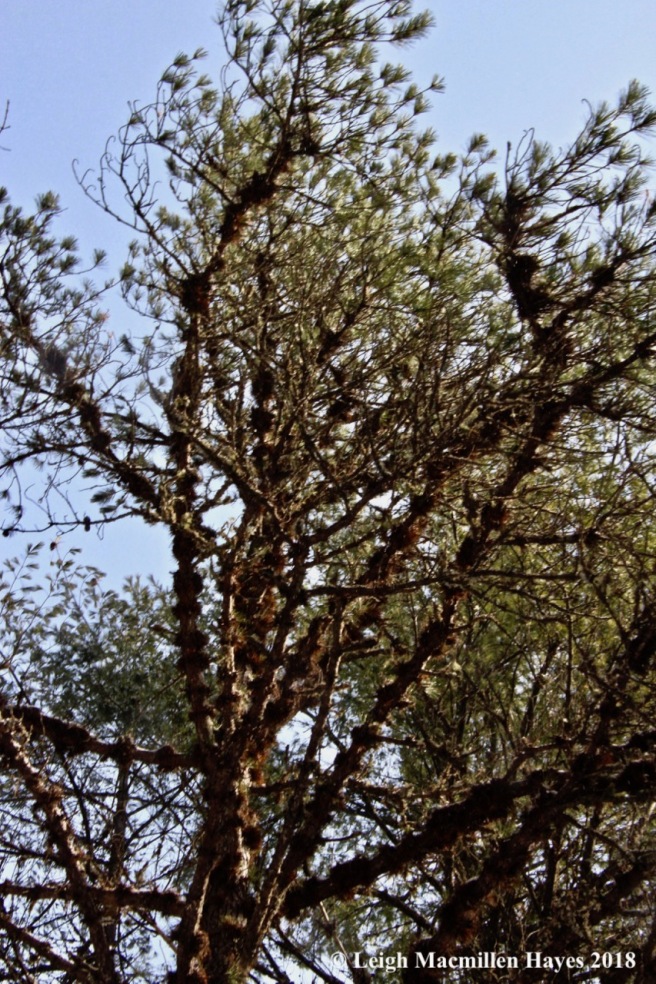
The Eastern white pine (Pinus strobus), strikes me as the majestic tree of our forest. Of course, it was once even more majestic. In the 1600s, the British Royal Navy blazed all of those two feet or more in diameter and within three miles of water with the broad arrow indicating they were to be cut, harvested and sent to England for ship masts. The blaze became known as the King’s Arrow in honor of King George I. At that time, the trees may have been 300-400 years old and over 200 feet tall. The oldest and tallest white pines in our current landscape are 80-100 years old and maybe about 100 feet tall.
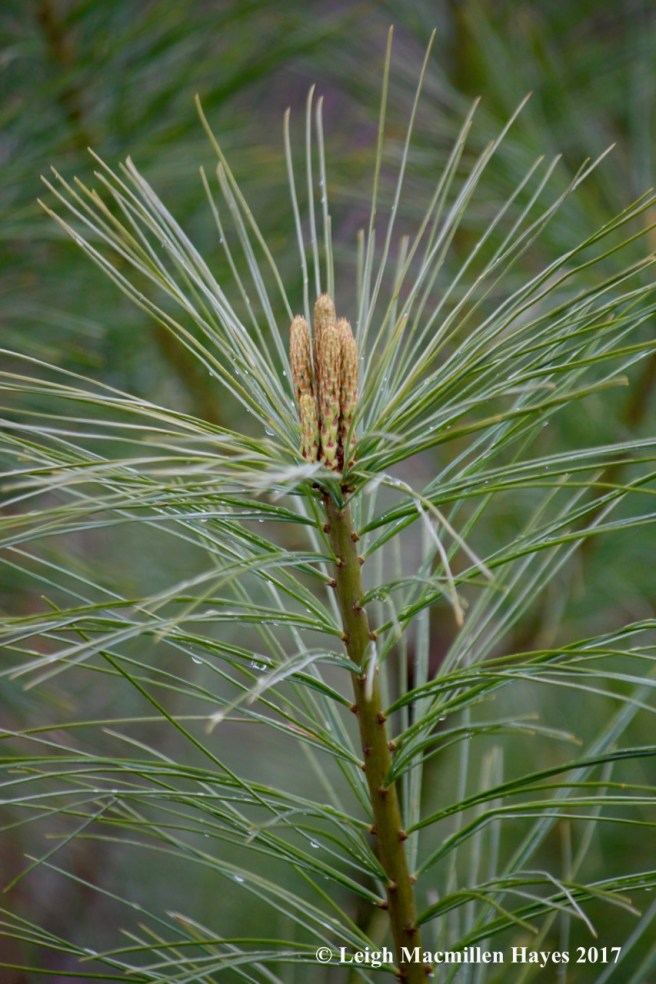

The three to five-inch white pine needles are blueish-green and bound in bundles of five. That’s easy to remember for you can spell both the tree’s name W-H-I-T-E with each needle or M-A-I-N-E for the white pine is our state tree.
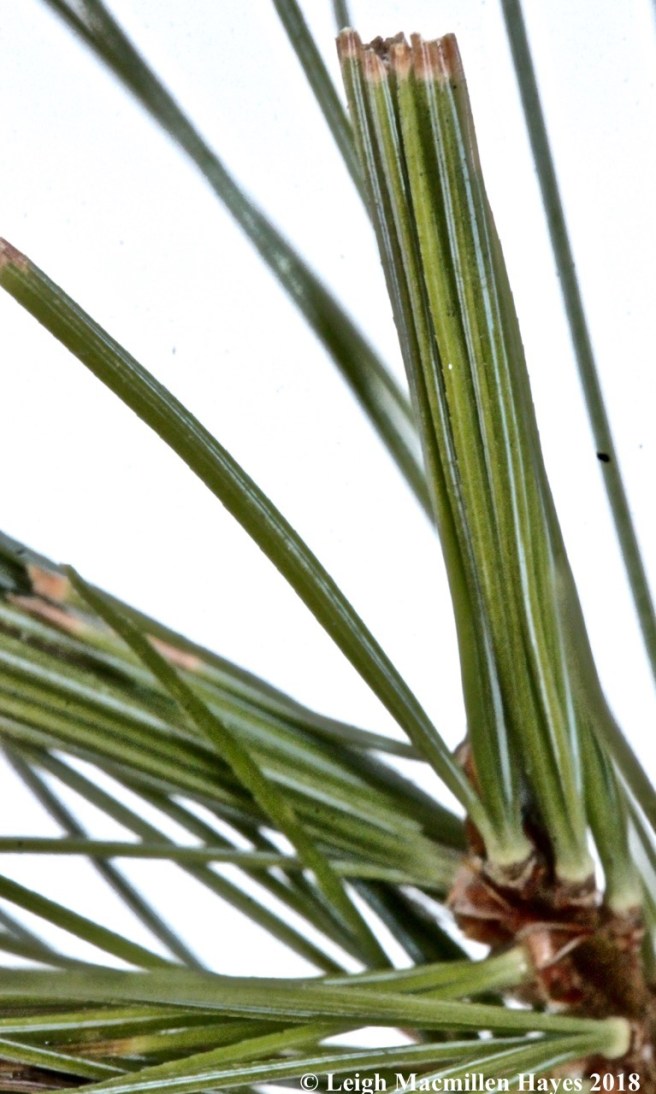

Occasionally, I’ve spotted trees with clumps of needles stuck together in such a way that they formed tubes. Actually, they were the tunnels created by the pine tube moth. Larvae hatched from eggs deposited on the needles during the summer. They used silk to bind the needles together, thus forming a hollow tube. Notice the browned tips–that’s due to the larvae feeding on them. Eventually the overwintering larvae pupate within the tube and emerge in April. Two generations occur each year and those that overwinter are the second generation. Fortunately, they don’t seem to harm the trees.

In addition, the arrangement of branches is another important feature of this white pines for they are arranged in whorls radiating from the tree’s trunk like spokes on a bicycle wheel, with each whorl representing one year’s growth. Sometimes on older trees that grew beside stone walls in pastures, the older branches remain and when topped with snow look like a spiral stairway to heaven.

On younger white pines, the bark has a greenish hue, but as the trees mature the bark turns dark gray to reddish-brown and forms into thick, vertical scales with furrows between. Upon the flattened ridges of the scales, look for a pattern of horizontal lines reminiscent of the lines on notebook paper.
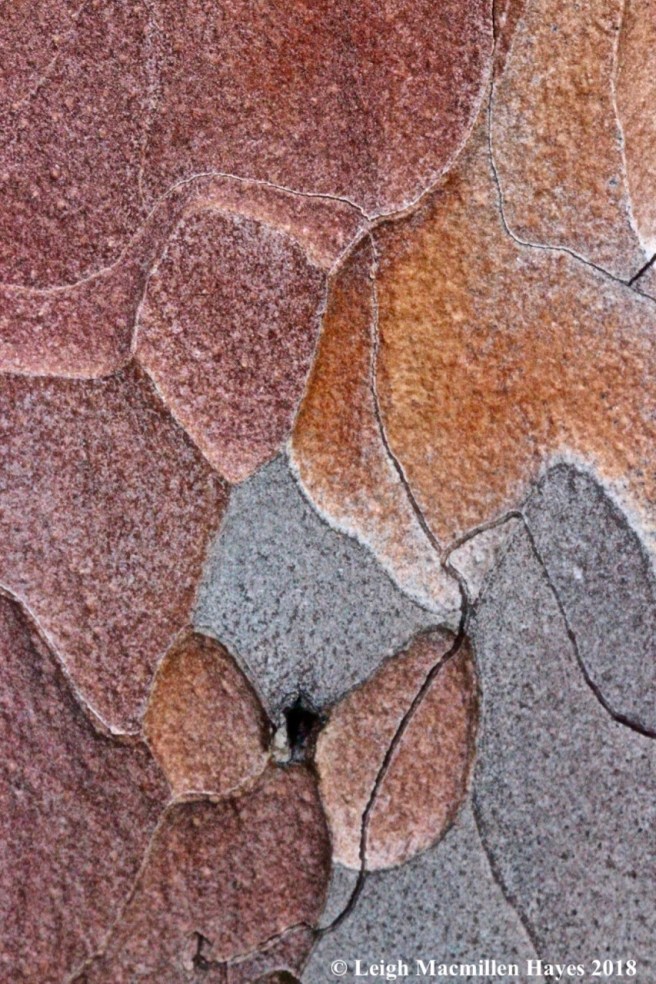

Red pine (Pinus resinosa) is a favorite of mine because of its bark, which reminds me of a jigsaw puzzle. Ranging in colors from faded orange to mottled red and grayish brown, its flaky flat scales hug the tree.
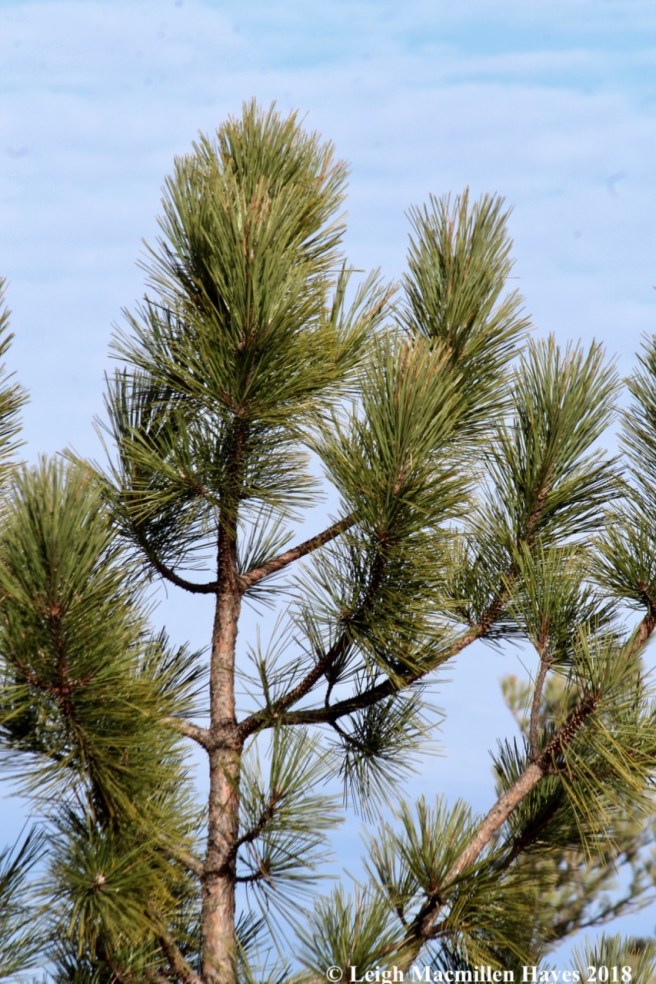

In a perfect world, red pine would produce three needles/bundle to spell R-E-D. Alas, the world isn’t perfect, nor is that the case with this tree. Instead, it has two dark green needles that are twice as long as those on a white pine and quite stiff. In fact, while a white pine’s needles are soft and flexible, bend a red pine needle and it will snap in half. Because of the needle arrangement on these two members of the Pinus family, from a distance I can name them. To my eyes, a white pine’s branch tips look like bottle brushes, while a red pine’s remind me of the brush Bert used to sweep chimney’s in Disney’s Mary Poppins.
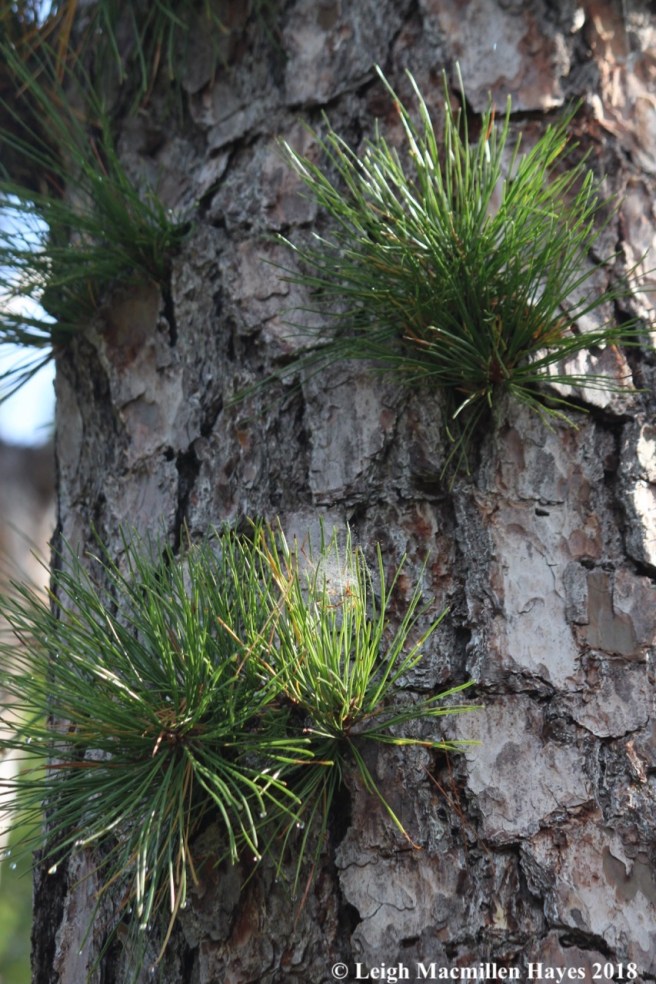

Another common pine in our area of Maine is pitch pine (Pinus rigida). This one is easy to confuse with red pine because the bark looks similar in color, though it strikes me as forming thicker plates. The name, pitch, refers to the high amount of resin within this tree.
It’s the needles of pitch pine that also add to its identification for they grow in bundles of three, like a pitchfork’s tines. The unique thing about this tree is that not only do the stiff, dark yellow-green needles grow on the branches, but they also grow on the trunk. If you spy a tree that you think may be a Red Pine, scan upward and if you see green needles along the trunk, then you’ve discovered a Pitch Pine.
Pitch pine is an important species for it is the only pine that is well adapted to fire and can even resprout.

Finally, for our native pines, and I can only think of a few local places where I’ve seen these, including along the Foster Pond Outlook Trail at Bald Pate Mountain in South Bridgton, is Jack pine (Pinus banksiana). It seems to prefer the coast and central northern Maine. But . . . walk Loon Echo Land Trust’s trail at Bald Pate, and see if you can spot them.
Jack pine has two yellow-green to dark green needles in each bundle so an easy way to remember its name: Jack and Jill. I don’t know about you, but I love mnemonic devices.

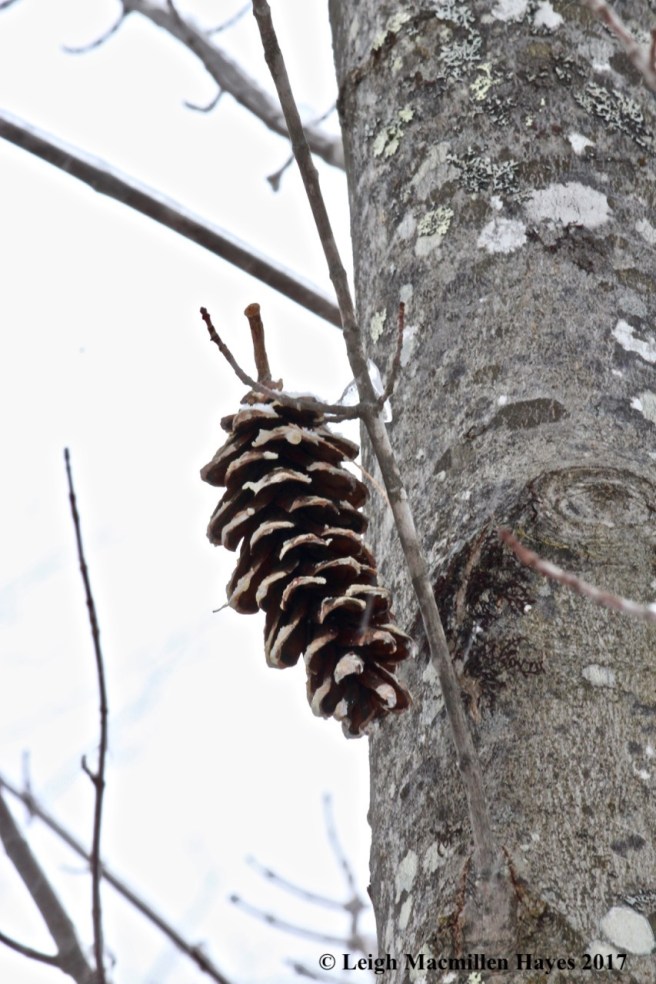
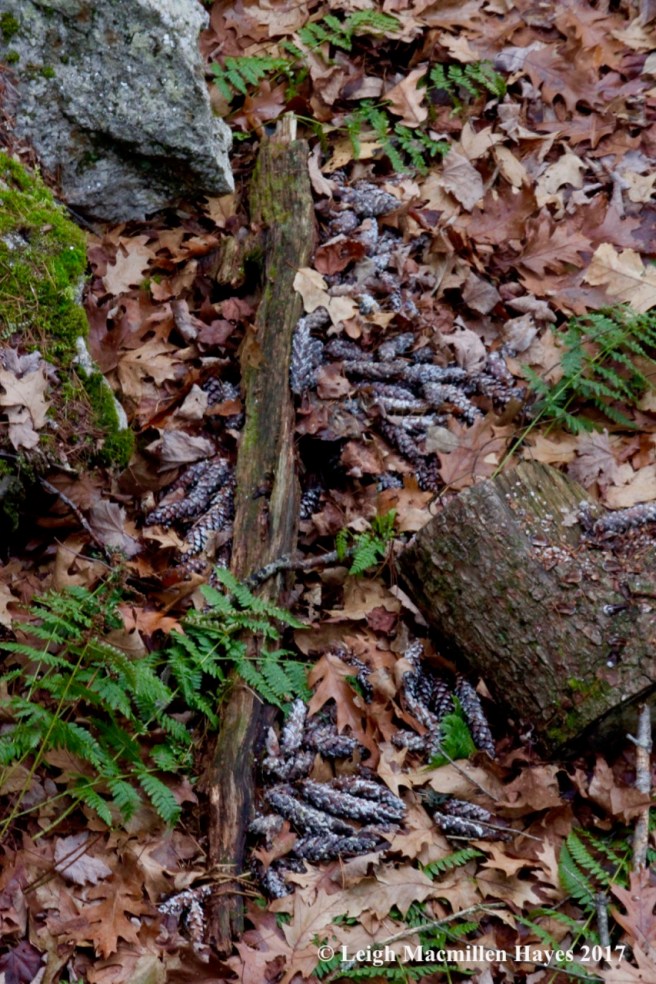
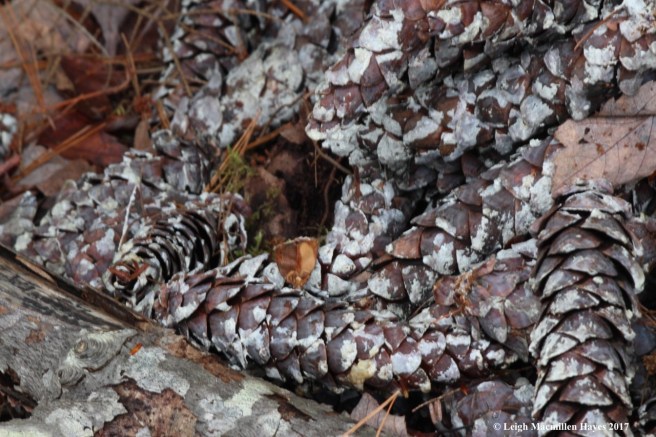
One last way to differentiate the pine trees is by their cones. Cones are the fruits of the trees and they consist of scales that protect seeds. When conditions are right, the scales will open to release the seeds, which have wings much like a maple samara, allowing them to flutter off in the wind and find their own spot upon which to grow. The line-up in this photo from left to right: white pine, red pine, hemlock.

White pine is easy to ID for it produces long, narrow cones, often coated with white sap. It takes two years for a white pine cone to mature.
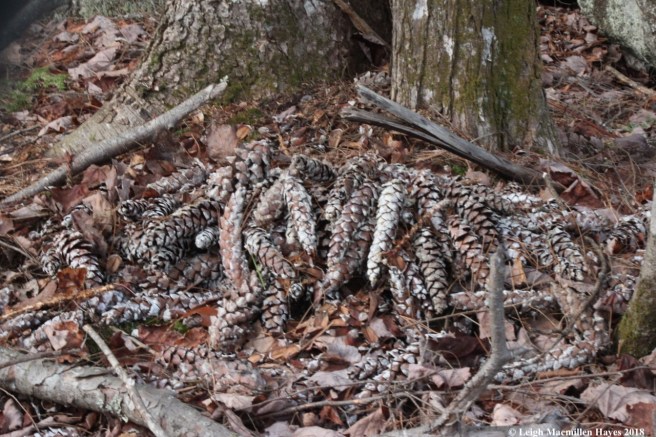

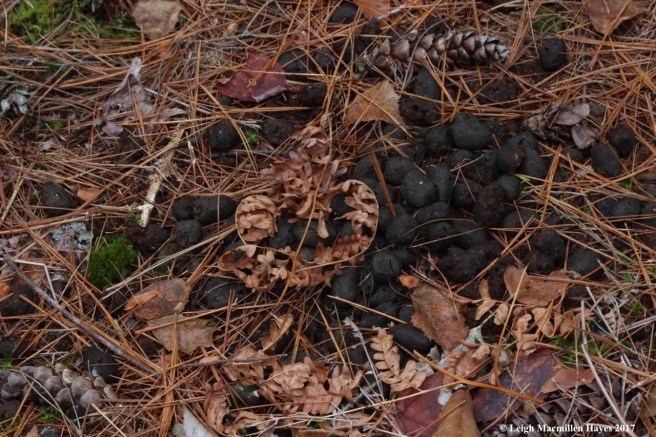
Red squirrels are known to gather mature cones and store them in a cache for winter consumption. During the winter, the squirrels tunnel under the snow to access the cache, then climb up to a high spot and remove each scale to reach the seeds. Left behind is a midden or garbage pile of scales and center cob of the cone.

Red pine cones are about two inches long and egg-shaped on short stalks.
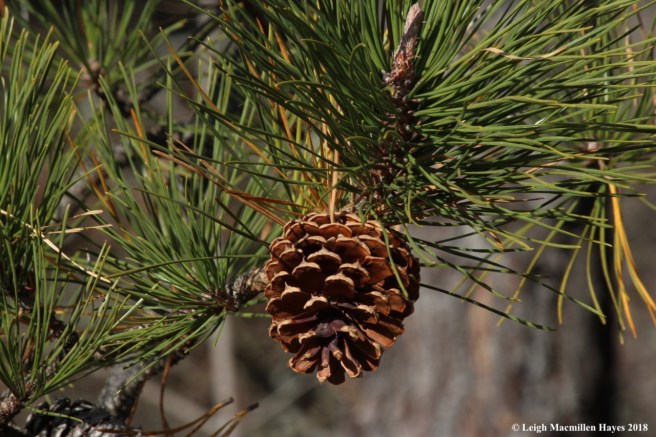

You can barely see the stalk of pitch pine cones that tend to be clustered together, but their key feature is the rigid prickle atop each scale tip. On Jack pines, the cones are about two inches long and slightly curved like a comma.
Before I move on to the other evergreens, I need to make one point. Members of the Pinus family produce pinecones. All other evergreens produce cones, but they aren’t pinecones because they don’t grow on pine trees.

Eastern hemlock (Tsuga canadensis) grows almost as abundantly as white pine. Often white pine, hemlock, balsam fir and spruce saplings can be observed growing together, and a perfect classroom situation evolves.
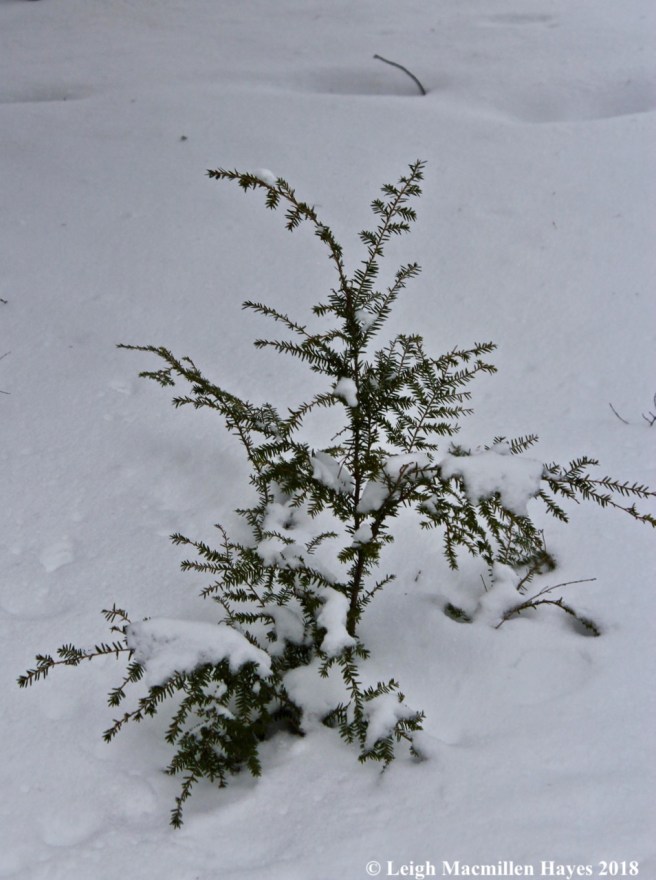

The hemlock is easy to ID once you realize its characteristics. To begin with, and especially noticeable in younger trees, is the drooping terminal shoot. In fact, all of the branches droop, providing the overall effect of a graceful tree.

Those sturdy, down-sweeping boughs also hold snow, thus creating the perfect spot for deer to hunker down under on a winter night.

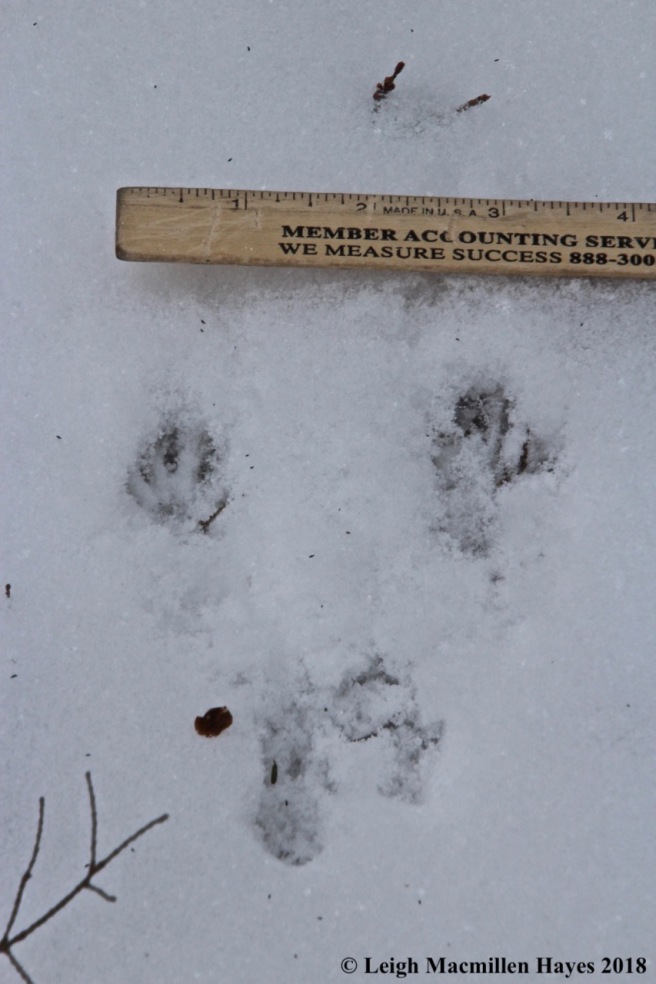
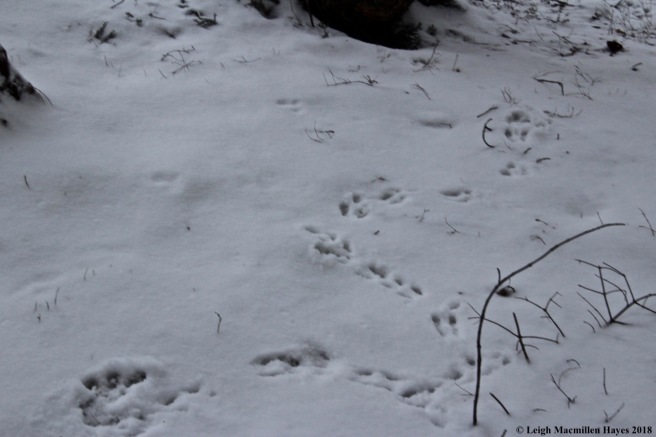
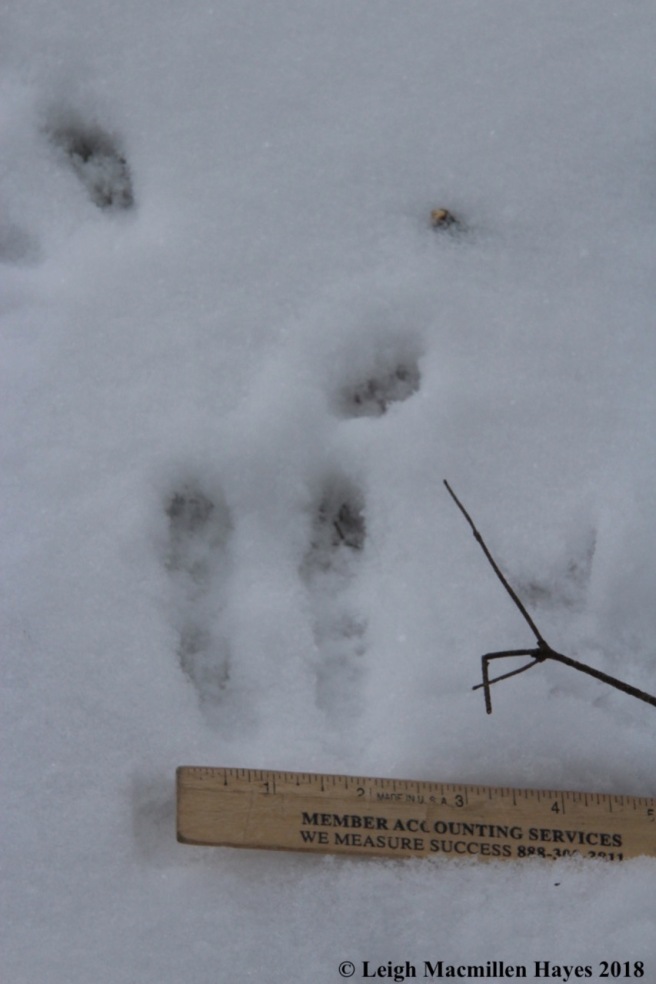
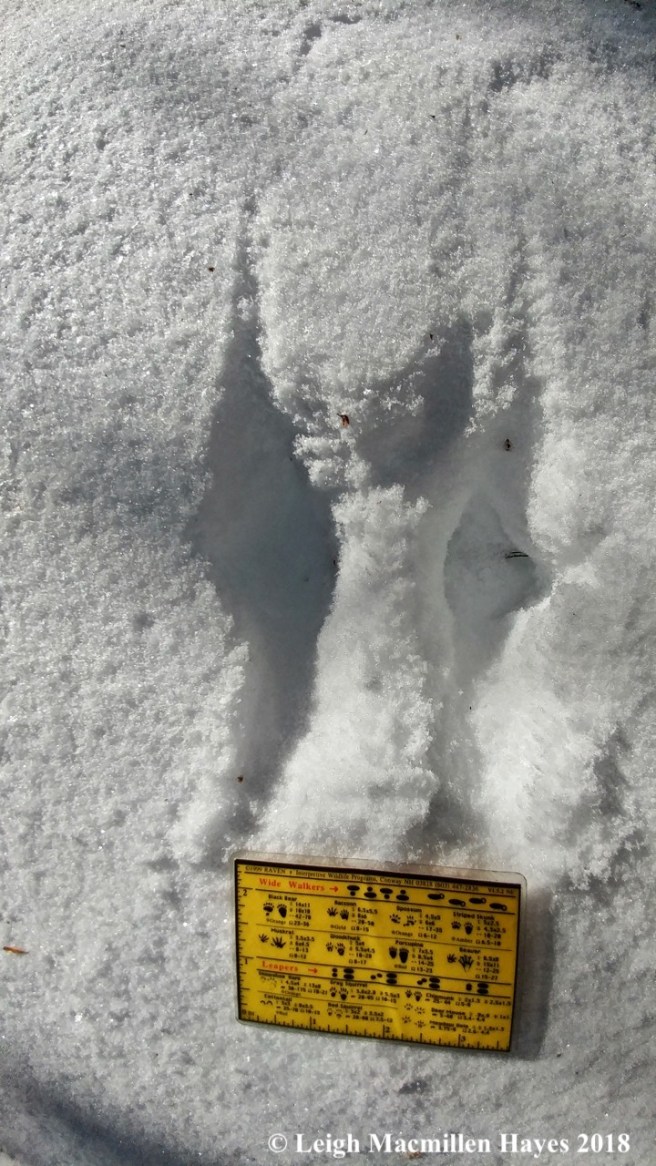
Another mammal that takes advantage of the hemlock is the porcupine. If you spy nipped twigs on the ground surrounding a hemlock, then it’s best to look up and make sure you won’t become a pin cushion should the animal fall.
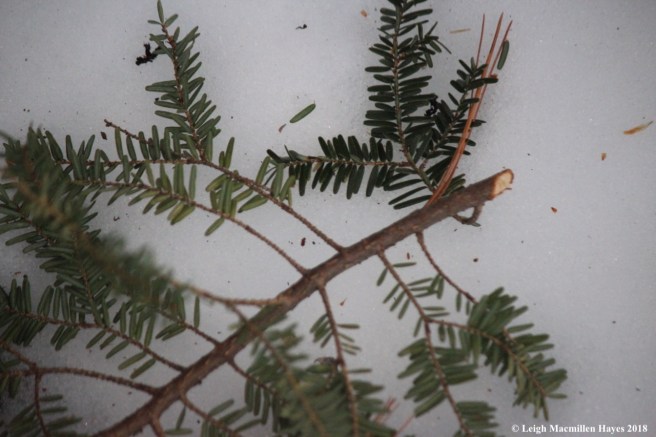

Typically, the downed hemlock twig features a cut made at a 45˚ angle.

The half-inch hemlock needles taper to a dull point. You may only see this with a hand lens, but each needle is attached to the twig by a short stem, aka petiole. And the needles extend outwards from both sides of a twig, thus giving it an overall flat appearance.

The bark on a hemlock, initially grayish and smooth, becomes cinnamon brown and scaly with age. I also enjoy looking at the inner bark that might be exposed by an injury, for its features various shades of reddish purple.

Hemlock cones are petite in comparison to pinecones, at only .75 inch in length. In the spring, their scales are blue-green, maturing to a tan by autumn.
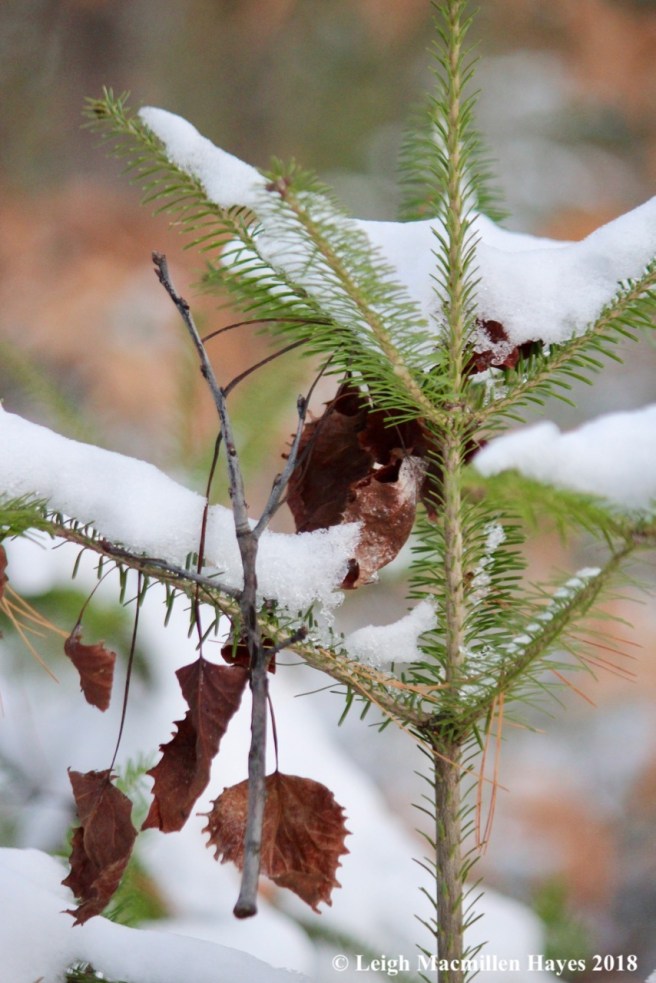

While the hemlock droops, a balsam fir (Albies balsamea) stands straight and tall as it forms a spire with a symmetrical crown.
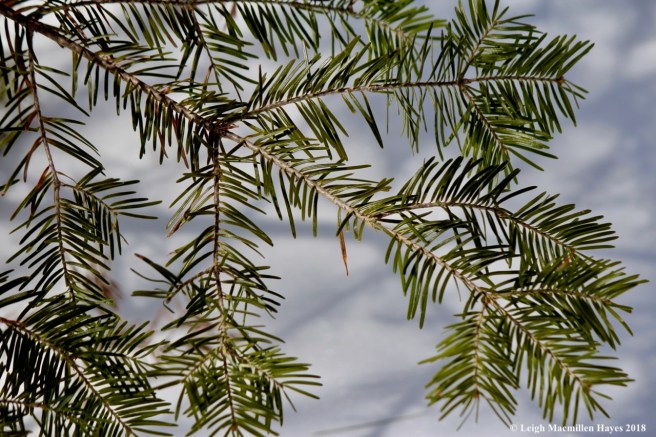

Like the hemlock, the needles are flat, but they differ in that they attach directly to the twig, are about an inch in length and some have a notch at the blunt end. The upper side is a shiny dark green, while the underside is silvery-blue.

The pale gray to green-brown bark of balsam fir is also different than the other evergreens. It has raised dashes, aka lenticels. All trees have lenticels that allow for the exchange of gases. On some trees, however, the lenticels are more noticeable. Balsam fir bark also is riddled with bumps or resin-filled blisters. Poke one with a stick and watch the pitch ooze out. Beware, it’s very sticky. And it smells like Christmas.

One other unique characteristic of a fir tree is that the cones point upward rather than dangling down. That, in itself, offers an easy ID.

The next family, the Picea or spruces, I find more difficult to distinguish in a crowd. Like balsam fir, the leaders or top sections point skyward giving it an overall pyramid shape, but its the idiosyncrasies within the family that sometimes stump me.
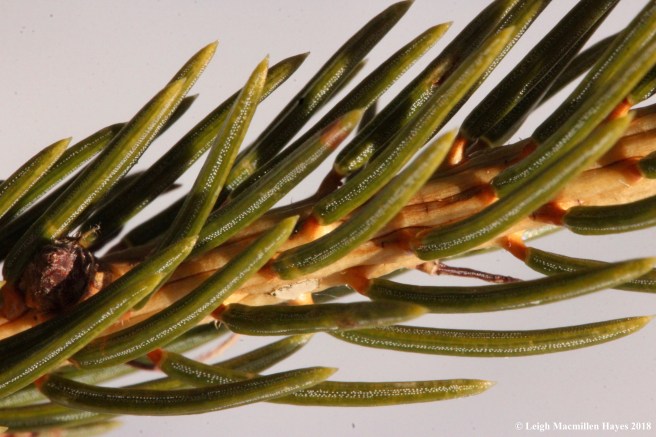

The one thing I am certain of is that they are spruces if their needles are sharp and pointed. Shake hands with a branch and if it hurts, it’s a spruce.
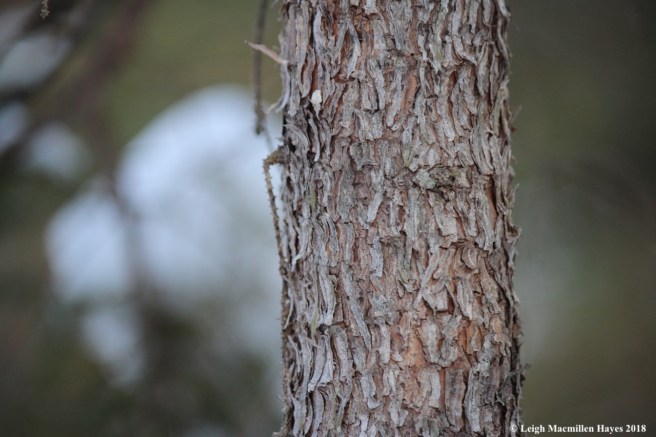

Spruce bark is broken into irregularly-shaped scales in general, and white spruce bark is gray to reddish-brown.
Again, I’m brought to things to remember when trying to determine whether I am looking at a fir or spruce—firs are friendly, spruces are spiky. Fir needles are flat, spruce needles are square.
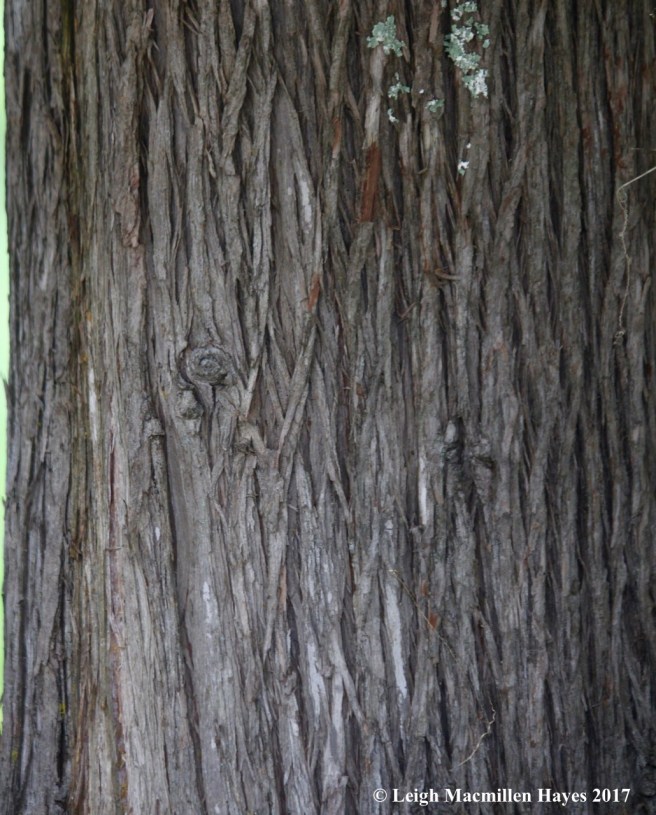
The only cedar tree native to western Maine is the Northern white cedar. Whenever I sniff its fragrant scent, I’m reminded of my mother’s cedar chest and the treasures it stored.

Northern white cedar (Thuja occidentalis) is also known as Eastern arborvitae. Its scale-like leaves appear opposite each other along the twig and have short, blunt points.
The cones are about a half inch long, oblong in shape and borne upright on the branches. Their scales are leathery, red-brown and notched. They also have a small spine on the tip.
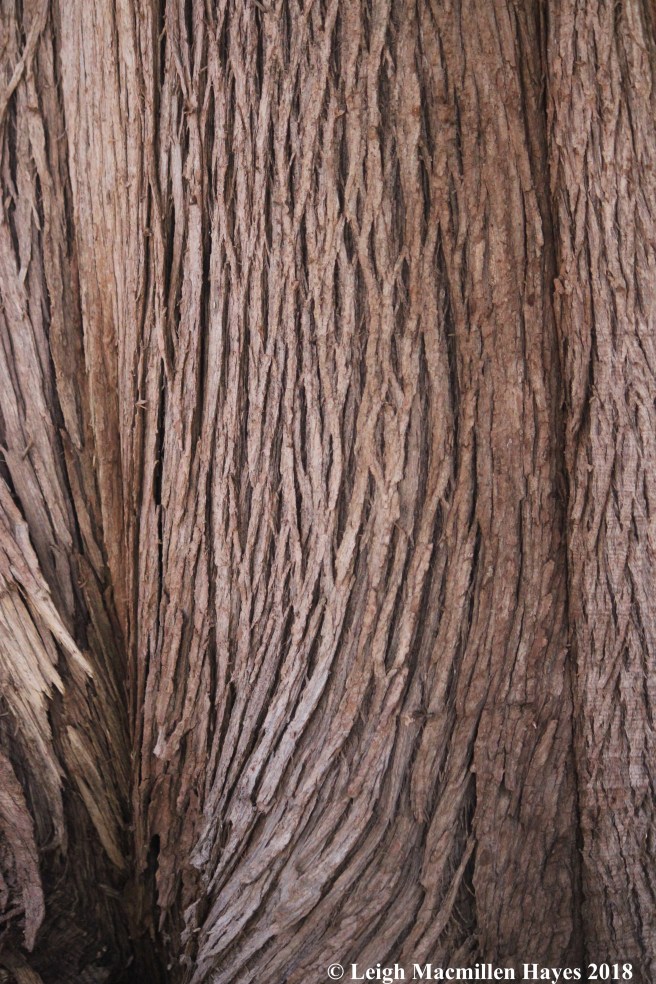

Again, the bark is fibrous, red-brown, which weathers to gray and features a diamond-shaped pattern. This small to medium-sized tree looks like a pyramid with a broad base and rounded top. It often features several main trunks.
And then there’s the tamarack.
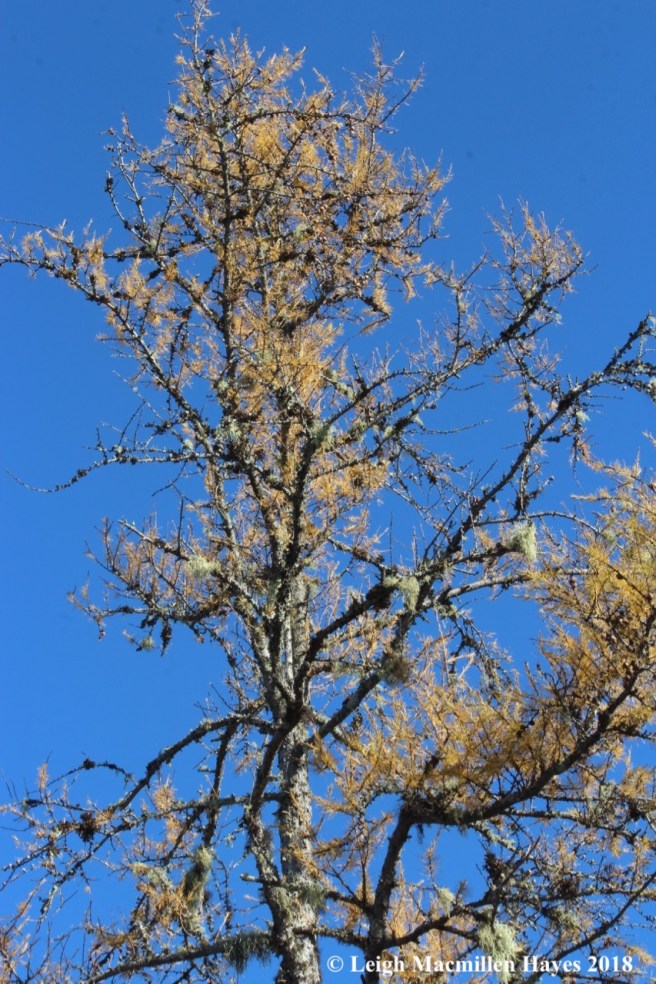

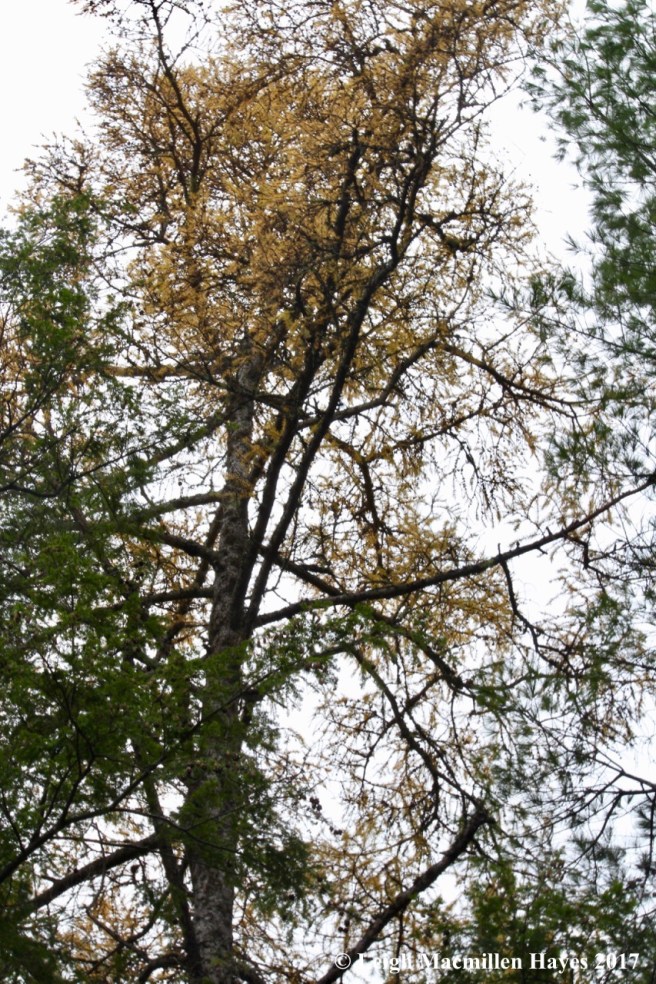
A tamarack or Larix laricina is a native deciduous conifer because it sheds its needles each fall, after they’ve turned a golden yellow, therefore it’s not really an evergreen.

I know how easy it is to look at the winterscape and think that everything looks the same in the almost monochromatic mosaic we call the woods.

But even in spring, as buds give way to leaves,

summer when so many greens dominate our world,
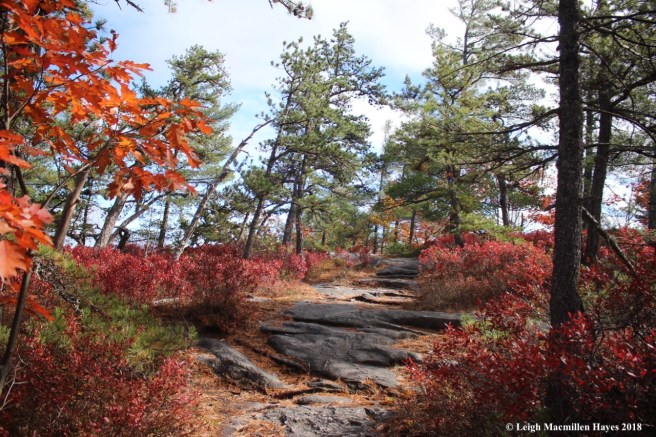

fall, when evergreens provide a contrast for autumn’s foliage,

and late fall, when the evergreens continue to be green as the broad leaves drop, these trees make a statement in the landscape.
Thanks to Creator, they are forever green.